What is the Repeatability of the Adaptive Gripper?

Posted on Aug 08, 2011 1:22 PM. 2 min read time
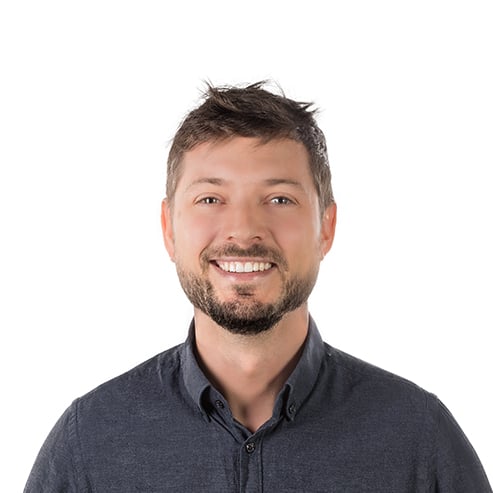
In a previous post, we described what robotic gripper repeatability is and how it is typically determined. Robotiq adapted the ISO 9283 norm of robot performance standards to measure the position repeatability of the Adaptive Gripper. This article presents the results and how they were obtained.
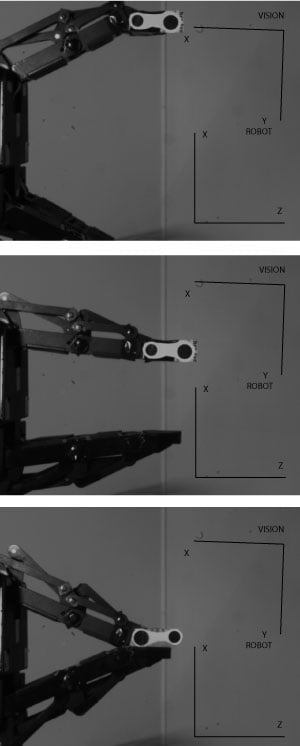
How did we measure repeatability?
The following hardware was used:
- FANUC M-710iC robot
- Robotiq Adaptive Gripper
- Vision target
- Mightex camera
- Vision software by the CRVI
Vision targets are installed on the side of the Adaptive Gripper fingertips (see image). The position of the target on a plane is measured by the vision system. The fingers are brought repeatedly (50 times) to two different positions: half closed and fully closed. We then use the formulas in our previous article on gripper repeatability to calculate the repeatability from the collected data.
The Results
- The gripper finger position repeatability (in fingertip grip) is 0.065 mm
- Note that we have also measured the repeatability of the vision system itself with fixed target and obtained 0.008 mm
- The repeatability of the robot in a plane was also measured by installing the target on the robot end-of-arm and is 0.024 mm
- The repeatability of the robot and the gripper combined is 0.072 mm
How do we compare to the competition?
Classic grippers, with no position control, typically offer a repeatability of around 0.01 mm. These values are of great precision but can't be directly compared as classic grippers can only do total open & close functions. Servo-electric grippers offer a slightly higher repeatability because they have the advantage of position, speed and force control. A typical 2 jaw parallel electric gripper can have a repeatability of 0.02 mm. The repeatability of the Adaptive Gripper is slightly higher as it has more fingers and more phalanges per finger. For many applications, this repeatability is more than sufficient to place parts precisely. For applications with even tighter tolerances, or when encompassing grips are prevalent, a fixed vision system can be used to measure part position inside the gripper after a part is picked.






Leave a comment