Intelligent Robotic Manipulator for Automotive Manufacturing

Posted on Aug 27, 2013 3:11 PM. 5 min read time
Robotiq’s team recently paid a visit to the Robotics Lab of Laval University and we found a lot of interesting projects. We already wrote an article on the statically balanced robot arm and there are other projects worth mentioning. Some of them concern industrial collaboration, i.e. developing solutions for companies. General Motors Canada is one of the important industrial partners of the University and we had the chance to see one of their prototypes.
GM asked the University to develop an intelligent manipulator featuring some aspects of collaborative robot that would help its employees to assemble car dashboards. They are pre-assembled in another plant and, when it is time to affix them in the car their weight can be up to 113 kg. Moreover, a dashboard is installed every 75 seconds. Its installation is very tricky because the dashboard is large and the whole part has to be insert in the car without damaging anything. This is the main reason why the process cannot be fully automated yet. So, the company needed a robotic tool that would help its employees with the manipulation and the installation of these large and heavy dashboards.
For this task, the assistance device needs 4 degrees-of-freedom; 3 translations and the rotation around the vertical axis. For human-robot collaboration, the speeds are limited at 1m/s for the horizontal translations, 0.25 m/s for the vertical translation and 1 rad/s for the rotation.
Here is a schematic of the whole system.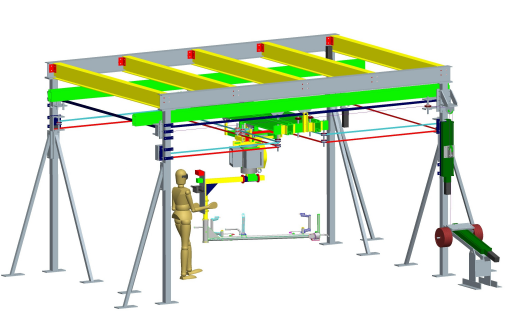
Mechanical Design
The main factors that were considered during the design of the assistance device were; how to reduce the overall mass and power needs of the prototype.
First, the motors are installed on the stationary structure instead of on the device itself and the power is transmitted by belt routings (or cable routing for the vertical axis). This reduces its weight and the inertia of the manipulator. All the axes are independent, so a displacement in one direction doesn’t induce a displacement in another.
Second, the vertical axis is designed with a counterweight to equilibrate the gravity effect. Also, the counterweight can move on a lever to compensate for the extra weight that the manipulator will lift. This way, the employee will never feel the weight of the the dashboard. The motors just have to work against the friction of the cable routing and the inertia of the device and its dashboard.
Third, the structure of the manipulator is made of aluminum to reduce its weight. A C-shape structure is used because the center of gravity for the manipulator is located on the axis of rotation. This reduces the inertia that the rotation can create. Moreover, this design allows for the reduction of the weight without compromising the robustness of the structure.
Watch a video introducing the main features of this intelligent manipulator.
Control Design
In order to make it move around, a special handle was designed. This handle is made of photo-interruptors and compliant mechanisms that will feel every movement issued by the operator. It can feel force precisely up to 40 N. For safety purposes, both hands are needed to make it move.
There are 4 operation modes for this Intelligent Assist Device Manipulator.
- Hands-off control mode: The manipulator moves by itself to, for example, go get the next dashboard to install.
- Hands-on control mode with payload: The employee can move the manipulator with the dashboard on it and, for example, insert it into the car to install it.
- Hands-on control mode without payload: Now that the dashboard is fixed in place, the employee can remove the manipulator from the car and move it to another position.
- Passive mode: To move the manipulator without using power from the motors or brakes. It might be useful to move it out of the way if there is a problem on the line.
This manipulator is an important component for robotic development. It allows for the study of different control modes in a human-robot collaboration. It also helps to develop, improve and test algorithms.
Website for the project: Intelligent Assist Device Prototype
Related Article: Robotics Lab at Laval University: Statically Balanced Robot Arm







Leave a comment