How to Set Up Your First Ever Screwdriving Robot

Posted on Apr 19, 2022 1:07 PM. 5 min read time
Are you keen to get started with your first screwdriving robot? The big question on your mind is probably… how do I set the robot up?
Will you have enough expertise or experience to install your own screwdriving robot?
What do you need to know to ensure the robot deployment is a success?
Thankfully, the process for deploying a screwdriving robot is extremely simple. In just a couple of hours (or quicker if you're super-efficient) you can have a working robot that performs a screwdriving task completely autonomously.
Setting up the robot is also very easy. But you need to know what you're doing.
Here is everything you need to know to set up your first robot screwdriver.
What you need to know to use a robot screwdriver
If you have never used a collaborative robot before, you might imagine that the robot deployment will be a complex, time-consuming job. This is an understandable perception of robotics — conventional robotic deployments took weeks or months to setup.
Cobots are extremely simple to set up. But it's true that some tasks are easier than others to deploy.
One of our most popular first projects for cobot automation right now is palletizing. This looks like a simple task (and it is) so people can easily imagine what it might be like to program the robot — the robot just picks up the box, then puts it down on the pallet.
By contrast, screwdriving looks like it would be a tricky task to automate. It seems fiddly, like it might be prone to errors.
Technical users with more robotics experience are happy to get stuck in with programming their screwdriving robot.
But screwdriving can be just as easy to deploy as any other cobot application… as long as you have the right screwdriving solution.

Are you ready for robotic screwdriving? 5 key questions to ask
Before you can start setting up your screwdriving robot, you need to determine if you're ready for automated screwdriving.
By clarifying your goals upfront, you can ensure that you are applying the robot to the correct screwdriving task.
Here are 5 questions to get you thinking about robotic screwdriving in the right way. You can also download a copy of these as part of our handy screwdriving checklist.
1. What are your current key challenges with your screwdriving operations?
First, identify what challenges you have been experiencing lately with your manual screwdriving that you think a robot could help you solve.
For example, are you having difficulties finding workers for the job?
Are there frequent worker injuries or competitive lead times you need to keep up with?
Clarity on your challenges helps you to achieve clarity with your solution.
2. What are your screwdriving needs?
Then, look at the technical specifics of your task.
What types of screws will you use? Are they ferromagnetic or not?
What performance requirements do you have? This can include requirements like cycle time, batch size, and daily production hours.
3. Who will be in charge of the automation project?
One key factor for all the most successful automation projects we've seen is that they have a single person managing the project. This person doesn't need to do everything alone, but they will keep the project moving.
Does this person have enough time to put into the automation project?
Do they have robotics expertise? They don't need to have any previous experience, but a bit of technical know-how can go a long way.
4. How will the project be beneficial for your business?
You should now look at your numbers. You want to ensure that your screwdriving robot can bring you a return on investment in a reasonable time frame.
Calculate the yearly cost of your existing manual robot screwdriving and compare this to the costs of the robotic screwdriving. You can use our free ROI calculator to help you with this calculation.
5. Does your application pass "the test?"
Finally, is your screwdriving application suitable for robotic automation?
You can find this out by entering details of your task in our Screwdriving Fit Tool. This questionnaire will look at the specifics of your task and assess its suitability for cobot automation.
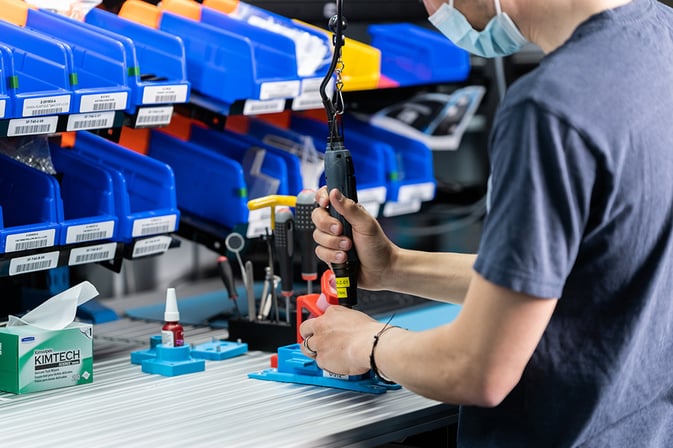
10 simple steps to install your first screwdriving robot
Now it's time to install and set up your first screwdriving robot.
With the Robotiq Screwdriving Solution, you can complete the installation in just 10 easy steps. These involve installing the robot itself, with the screwdriving tool, and then the automatic Screw Feeder.
5 steps to install the robot screwdriver
First, install the screwdriving robot.
This involves the following 5 steps:
- Mount the coupling for the screwdriving tool onto the robot arm.
- Mount the screwdriving tool onto the coupling.
- Wire the pneumatics. This is used to pick up the screws if the screw is non-ferromagnetic.
- Select the screwdriving bit that corresponds to your application.
- Attach the vacuum sleeve to the coupler.
That's it! The robot is now ready for programming.

5 further steps to install the automatic screw feeder
Before you can run your screwdriving task completely automatically, you also need to install the Screw Feeder. This will supply screws to the robot during the operation.
These are the 5 steps for setting up the Screw Feeder:
- Place the Screw Feeder on a flat work surface.
- Secure its position with the mounting brackets.
- Align the Screw Feeder on its shoes.
- Ensure the device is level.
- Adjust the following 4 components: screw singulator, rail, brush, and screw head clearance.
Now the Screw Feeder is also ready!
The easy way to learn to program your robotic screwdriver
Your robot screwdriver is now set up. But how do you program it to perform your screwdriving task?
The easiest way to learn about this is in our free eLearning course.
In the course, applications expert Mathieu Bélanger-Barrette takes you through the entire process of setting up and programming the Robotiq Screwdriving Solution. He also shows how to program the robot in just 8 minutes!
What questions do you have about robotic screwdriving? Tell us in the comments below or join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, or the DoF professional robotics community.




Leave a comment