Classification of Robotic Grippers and the Next Generation

Posted on Jan 14, 2014 in Robot Grippers
2 min read time
In the world of robotics, both the industry and application environment determine the specific tool used at the end of a robot arm. This tool varies in definition from an EOAT (end-of-arm-tooling) to a manipulator or gripper. As automation applications become more complex and robots continue to be utilized for efficiency, the need for more versatile, dexterous grippers has emerged. Traditional grippers have features or classification criteria that are commonly given to them.
Classification Criteria of Traditional Grippers
- Types of Motion
- Angular
With angular grippers, the fingers close toward each other by rotating around an axis. - Parallel
With parallel grippers, the fingers will approach each other remaining parallel.
- Angular
- Number of Fingers
The vast majority of traditional grippers have two “fingers”. In fact, most of these fingers are not articulated. Other grippers can have 3 or 4 concentric fingers
- Actuation
Depending on application requirements, the gripper can be actuated by electric motors, pneumatic or hydraulic valves. - Size
As there are a wide variety of sizes for robots, there is an equivalent variety of gripper sizes.
- Pinch Force
Because traditional grippers rely on friction to hold parts, pinch force is an important feature.
Next Generation of Grippers
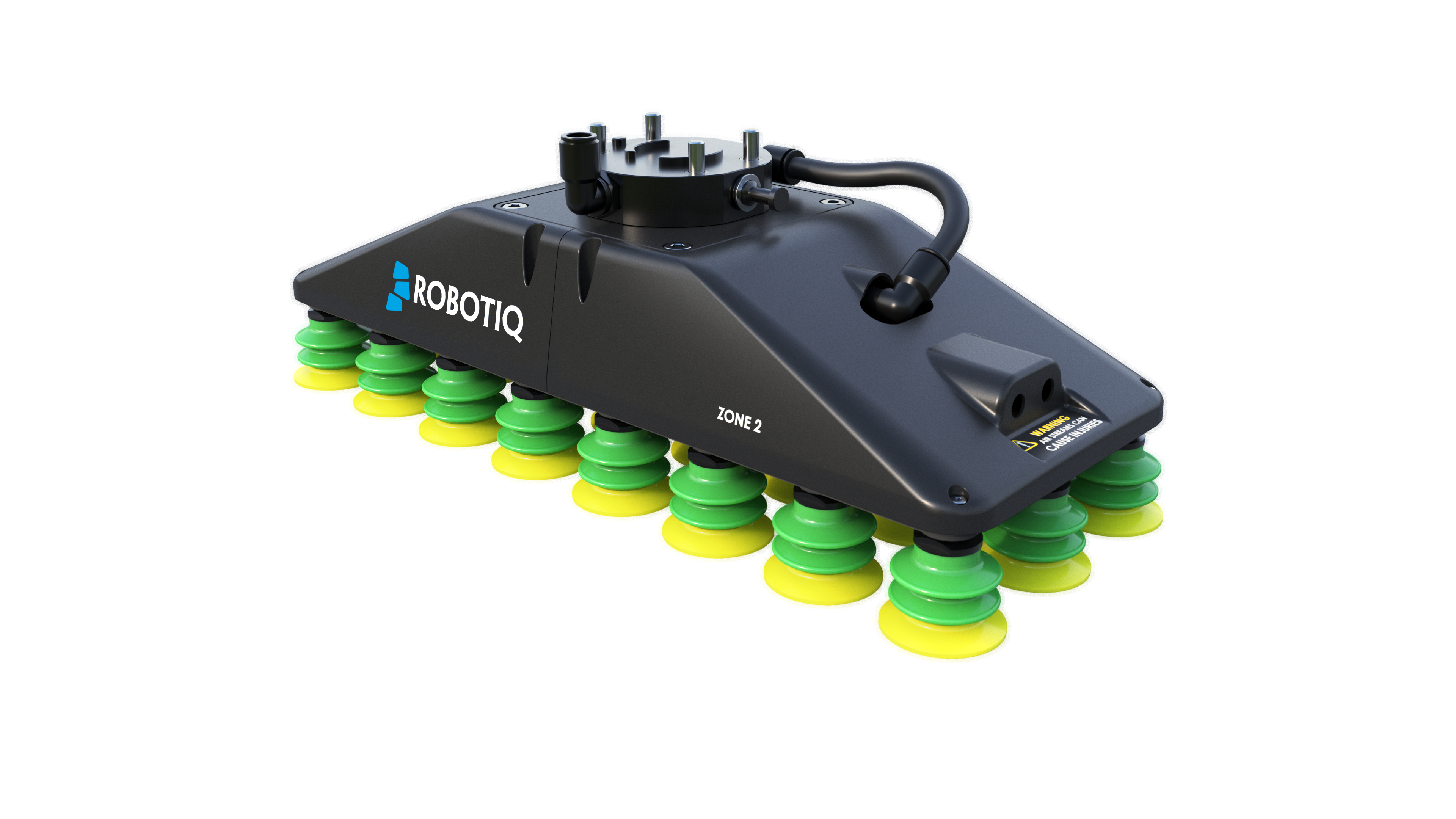
A new generation of grippers have entered the market. These dexterous grippers are a unique convergence between grippers and hands. They typically have articulated fingers that can adapt to the shape of different objects. One example of such a gripper is the Robotiq Adaptive Gripper.


These dexterous grippers will not replace all conventional grippers, they find their strongest use in applications where several traditional grippers would have to be used in conjunction with a tool changer to be able to properly grasp many different parts. The ability to use one tool for several applications (parts handling, parts transfer and sorting, picking and placing, kitting, etc.), or in the same work cell for a range of parts, greatly reduces tool changing time and setup costs.

.jpg)




Leave a comment