How to Choose the Right Power Source for Your Gripper?

Posted on Apr 21, 2015 in Robot Grippers
4 min read time
Power source is the backbone of all electrical appliances surrounding us. The main role of a power supply is to adapt the incoming high voltage alternating current (AC) to safer low voltage direct current (DC), like those used in many devices around us. The present article is about what you need to look at when choosing a power supply for your Robotiq device.
As one of my former professor told me back in the day. 'When there's an electrical issue, most of the time the power source is at the root of the problem'. Choosing the right power supply will help ensure that your robot gripper functions properly.
Understanding Specifications
Power supply can have many different specifications, let's look at the most important ones:
Input Voltage
Nowadays, a lot of power supplies can handle voltages ranging from 100V to 240V at frequencies between 50 Hz to 60 Hz. This ensure that, almost wherever you are in the world, the power supply will support the available outlet voltage and frequency. If the power supply you choose doesn't support this range, care must be taken to match the input of the power supply to the voltage and frequency of your regions electrical output. Indeed, if you planned to connect it to an outlet socket, don't forget to match the plug type with your region. Below is a map of standard voltages across the world.

For a complete list of voltages, frequencies and plug types by country, see the following link.
Output Voltage
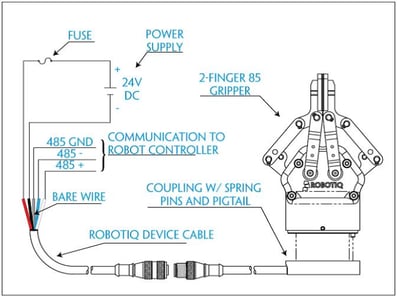
When selecting the power supply for your gripper the output voltage must match the gripper’s recommended voltage.
Output Current or Power Capacity
Generally, the capacity of the power supply will be express as a current capacity and/or power capacity. You can easily transfer from one to the other with the following equation:
In the Robotiq gripper datasheet, you'll need to look for information about the peak power or current needed for the gripper. Then, choose a power supply to fulfill the gripper requirement. But normally, it is suggested to crank up the source capacity to provide a security factor of around 1.2, because depending on the quality of the power source, some sources might not react as expected at their maximum rated power. Also be careful about power minimums as some low quality sources might need a minimum consumption in order to maintain their specified voltage. If the minimum consumption is not respected, the power supply might provide a higher voltage than rated and potentially damage your gripper.
Fuse Selection
The goal of introducing a fuse or a mini circuit breaker (MCB) between the power supply and the cable is to protect the cable from overheating and potentially catching fire if an overload or a short circuit happens. But it is good to know that a fuse or a MCB will not trip instantly when its nominal current is exceeded. For this reason, the fuse nominal current must be selected so the following relation is respected:
Gripper current < Fuse nominal current < Cable continuous current rating
Take note that the rated current of the fuse and the cable is given for a specific ambient temperature. If the ambient temperature of the application exceeds this temperature rating, current specification should be derated. See your fuse and cable datasheet for this information. In any case, Robotiq recommends a fuse for each of its grippers. The details of which can be found in their respective user manual.
For further explanations on this subject, see section 1.3 to 1.6 in this reference.





.jpg)

Leave a comment