How Do Collaborative Robots Affect the Supply Chain?

Posted on Jan 30, 2018 in Collaborative Robots
4 min read time
Opportunities to take advantage of collaborative robots exist throughout the supply chain, including manufacturing and warehousing operations. Implementing robotic systems can improve efficiency, reduce errors, increase safety by relieving humans from dangerous tasks, and reduce machine downtime. Compared to traditional industrial robots, the latest collaborative robots are better suited to high mix, low volume production, meaning they can be used to meet variable demand and for just-in-time inventory processes.
 Cobots can help deliver unsual big orders in time
Cobots can help deliver unsual big orders in time
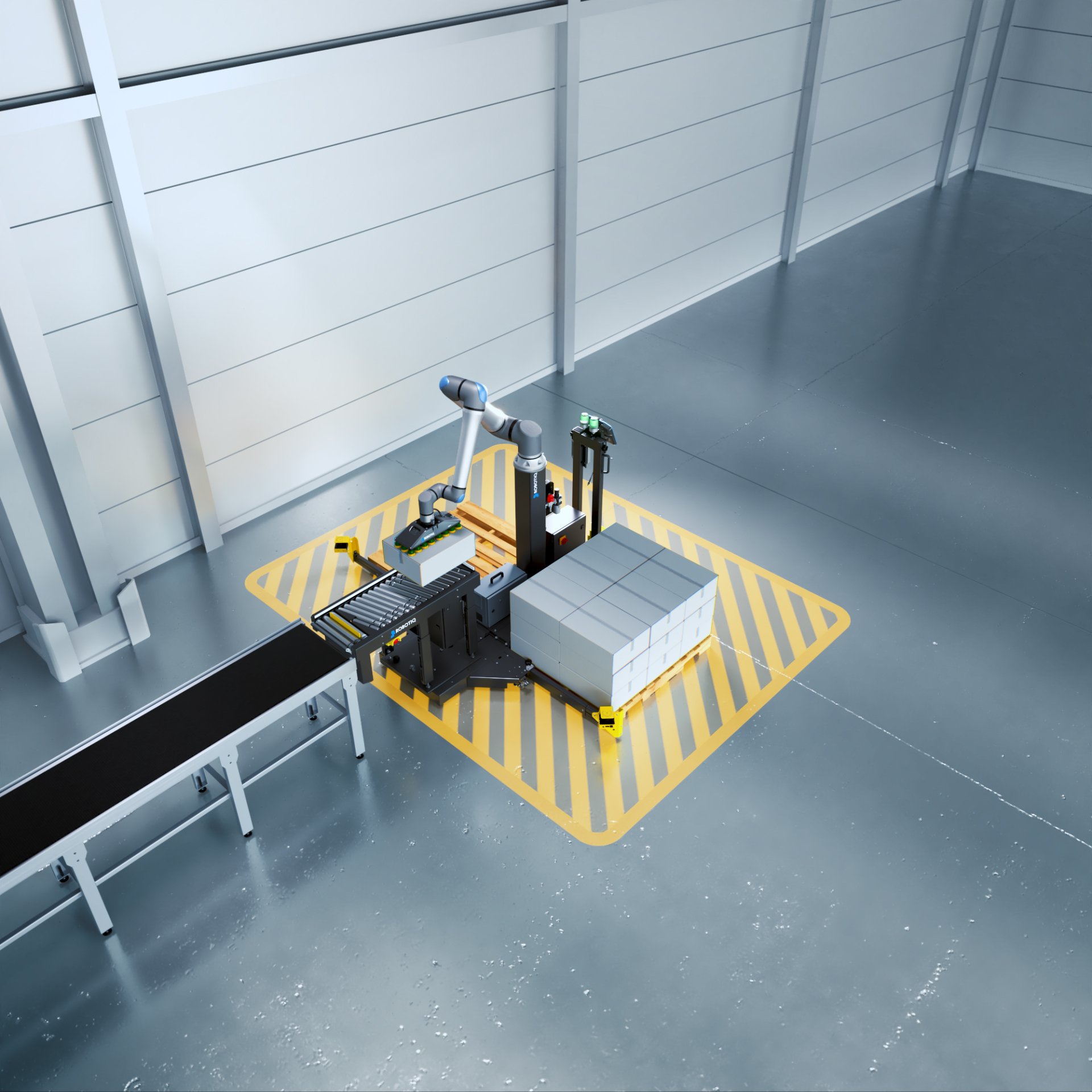
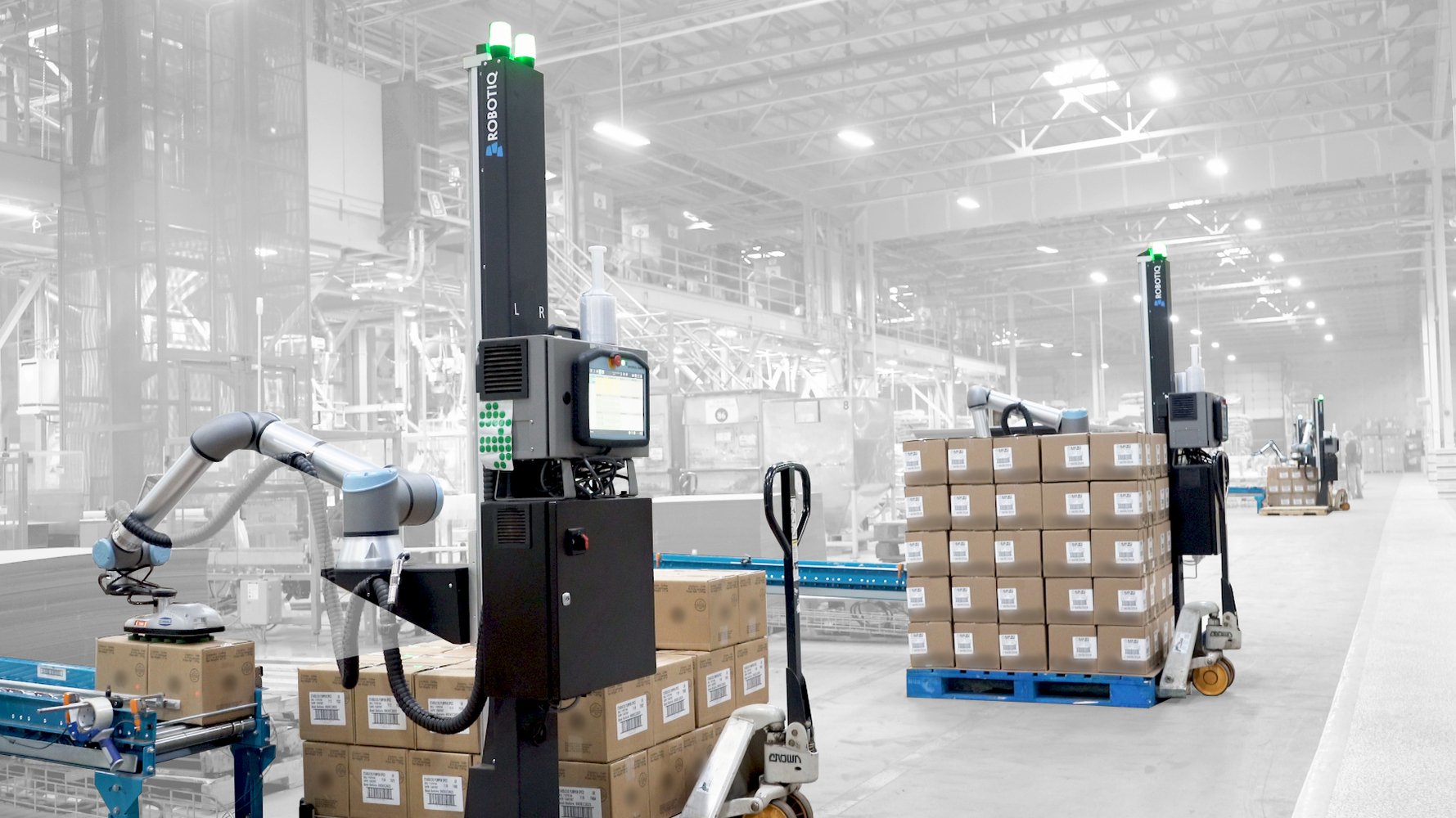
Robots can offer advantages in packing and palletizing tasks
Whether companies are looking for automated solutions to improve efficiency or to solve a labor shortage problem, robotic solutions are becoming more attractive for packing and palletizing applications. Robots can either be stationary or mounted on AGVs (automated guided vehicles).
Amazon has been using robots in its warehouse for years. A 2017 nytimes.com article reported that Amazon was using more than 100,000 robots for a range of warehouse tasks including picking and palletizing. Operations that require lifting and moving heavy loads such as palletizing and shelving are ideal areas to implement robotic solutions.
The supplychaindigital.com article, Automation and robotics: The supply chain of the future explores how DHL is using robotics in its supply chain, specifically in picking, packing, and sorting operations.
Collaboration levels and safety requirements vary depending on the application. Often, you’ll see safety caging separating humans from the areas where AGVs are moving at high speeds; but other applications have slower-moving, force-limited robots that will slow or stop when it detects a person in proximity. This case study describes an OTTO that travels safely around humans and forklifts.
Universal Robots provides an overview and video of using collaborative robots for packaging and palletizing, with a human working near the robotic arms.
Collaborative robots are evolving to overcome picking challenges
Picking can be challenging for robots, but as this wsj.com article reports, automated picking is evolving. For several years, the Amazon-sponsored annual robotics challenge has offered a cash prize to the team that designs a winning automated picking solution. One of the problems with picking is identifying disordered items of varying shapes. If the robot needs to pick the same item consistently, the operation is less complex than picking a variety of different shapes and sizes and flexible or fragile material.
Vision systems are making identification easier for robots, helping to solve one of the major picking issues. This case study describes how a Wrist Camera was used with a Robotiq 2-Finger Gripper to solve a picking problem where the parts were not presented in the same position.
As autonomous mobile robots and robotic picking solutions continue to evolve, the supply chain will benefit. A Forbes article about hot supply chain technology in 2017 says, “The combination of mobile robots and picking arms is potentially revolutionary.”
More supply chain technology ideas
Packaging Digest provided a high-level roundup of takeaways from a collaborative robot panel at the March 2017 Advanced Design and Manufacturing event, including ideas such as rethinking plant layouts and looking at collaborative workstations.
Another interesting technology development for supply chain is using drones for inventory management. Thanks to their accuracy and speed reading RFID tags, drones could continuously monitor inventory, helping to solve the costly inventory shrinkage problem.
When looking for ways to improve supply chain performance using collaborative robots, the lean robotics methodology is an excellent approach. Re-evaluating tasks and looking at cell redesign shows how robots and humans can best work together collaboratively to produce value. An example of how human /robot collaboration increased productivity is demonstrated in the Robotiq/Saint-Gobain case study. In this case, a polishing task that was unpleasant and even painful for humans was done by a collaborative robot, freeing the operators to work on other tasks and increasing capacity by 30%.
Companies ranging from small startups to multinationals are taking advantage of the efficiencies gained by deploying effective robotic supply chain solutions. Take pictures of how your warehouse and manufacturing operations are running now so you have a historical record. The supply chain promises to be almost unrecognizable in the near future.






Leave a comment