Industrial robots: What are the different types?


An industrial robot commonly refers to a robot arm used in a factory environment for manufacturing applications. Traditional industrial robots can be classified according to different criteria such as type of movement (degrees of freedom), application (manufacturing process), architecture (serial or parallel) and brand. Then there is also a new qualifier for industrial robots that can be collaborative or not. This article presents the different classifications with some examples.
Industrial robots with different types of movements
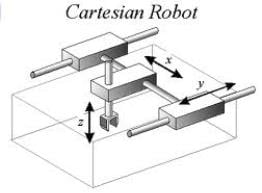
Cartesian robots
Cartesian robots are robots that can do 3 translations using linear slides.

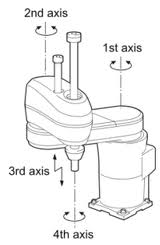
Scara robots
Scara robots are robots that can do 3 translations plus a rotation around a vertical axis.
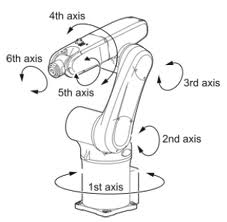
6-axis robots
6-axis robots are robots that can fully position their tool in a given position (3 translations) and orientation (3 orientations)
Redundant robots
Redundant robots can also fully position their tool in a given position. But while 6-axis robots can only have one posture for one given tool position, redundant robots can accommodate a given tool position under different postures. This is just like the human arm that can hold a fixed handle while moving the shoulder and elbow joints.

Dual-arm robots
Dual-arm robots are composed of two arms that can work together on a given work piece.

The type of movement is dictated by the arrangement of joints (placement and type) and linkages.
Industrial robots for different applications
The application is the type of work that the robot is designed to do. Robot models are created with specific applications or processes in mind. Different applications will have different requirements. For instance, a painting robot will require a small payload but a large movement range and be explosion proof. On the other hand, an assembly robot will have a small workspace but will be very precise and fast. Depending on the target application, the industrial robot will have a specific type of movement, linkage dimension, control law, software and accessory packages. Below are some types of applications:
Welding robots

Material handling robots
 Palletizing robot
Palletizing robot

 Painting robot
Painting robot

Assembly robot

Serial or parallel industrial robots
Serial robots are the most common. They are composed of a series of joints and linkages that go from the base to the robot tool.
Parallel robots come in many forms. Some call them spider robots. Parallel industrial robots are made in such a way that you can close loops from the base, to the tool and back to the base again. It's like many arms working together with the robot tool. Parallel industrial robots typically have a smaller workspace (try to move your arms around while holding your hands together vs the space you can reach with a free arm) but higher accelerations, as the actuators don't need to be moved: they all sit at the base.

Industrial robot brands
There are many industrial robot brands. The largest ones will have a complete range of robots for different applications and at different sizes. The smallest companies usually target a specific size or application range. Examples of industrial robot brands are:
To summarize all of the above, it is possible to have for instance:
- Scara movement, packaging, parallel, ABB robot
- 6-axis, welding, serial, Motoman robot
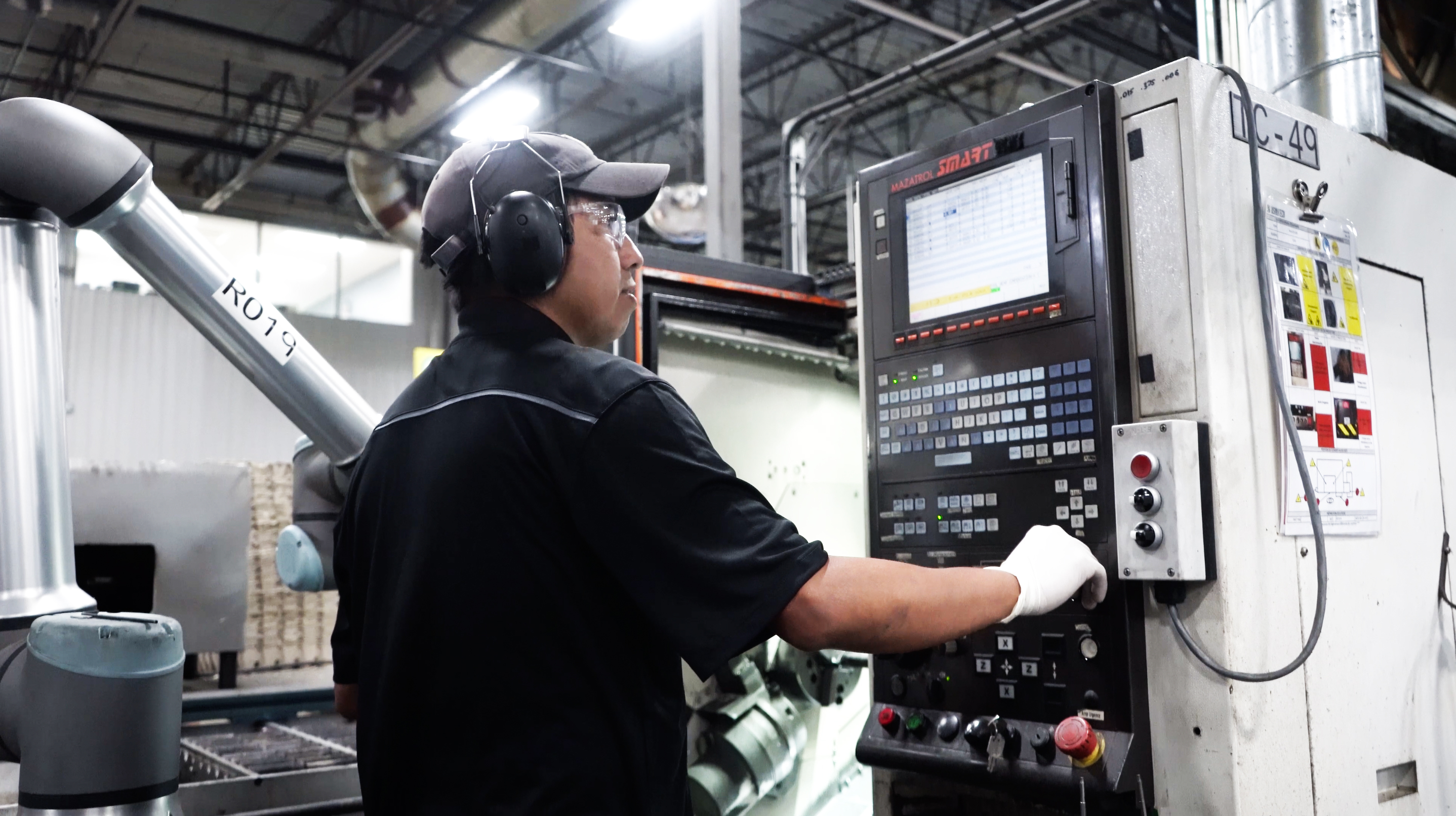
The latest generation: Collaborative industrial robots
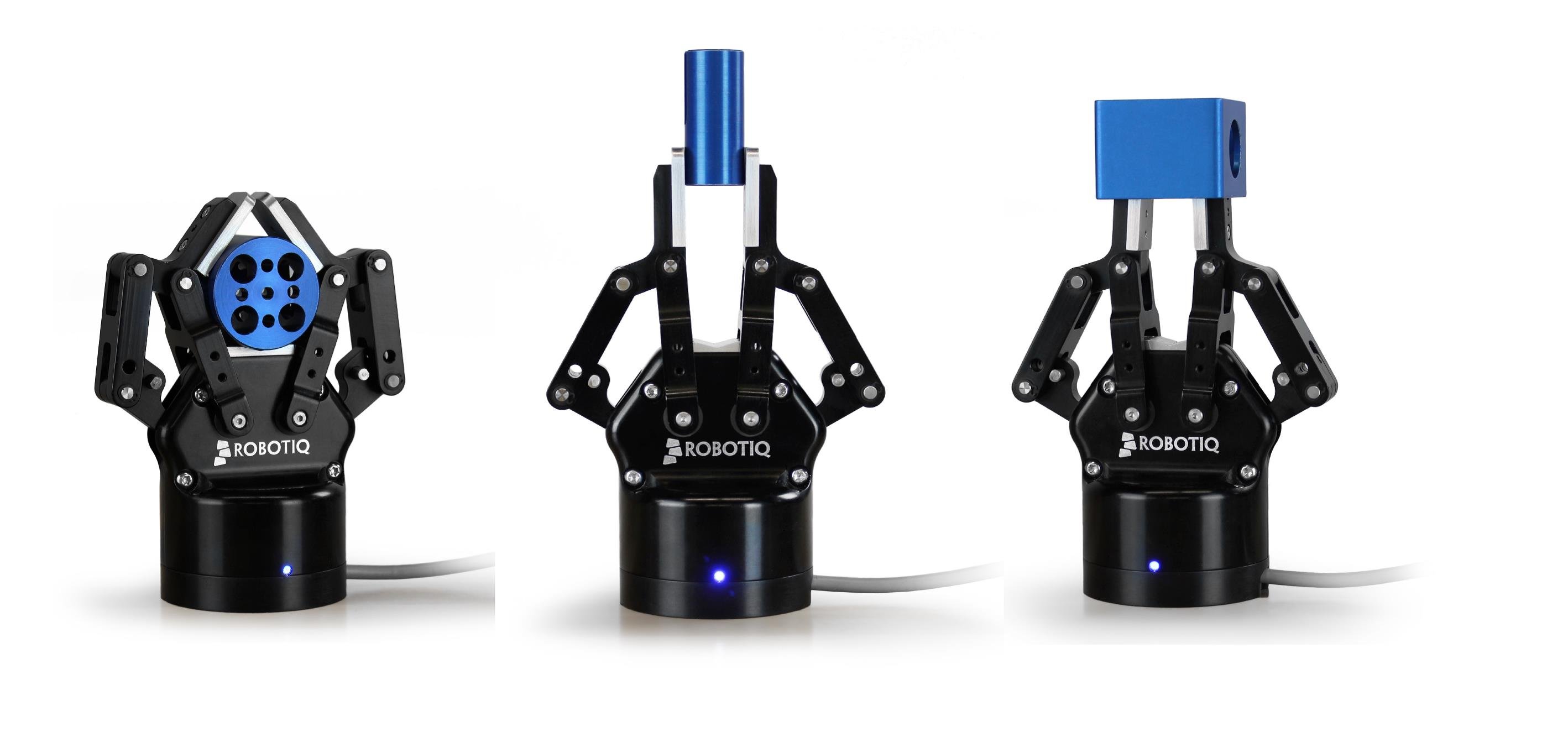
There is a new qualifier that has just recently been used to classify an industrial robot, that is to say if it can collaborate with its human co-workers. Collaborative robots are made in such a way that they respect some safety standards so that they cannot hurt a human. While traditional industrial robots generally need to be fenced off away from human co-workers for safety reasons. Collaborative robots can be used in the same environment as humans. They can also usually be taught instead of programmed by an operator. Examples of collaborative robots are:







Leave a comment