How to Prove a Robot's ROI with Analytics

Can key performance indicators (KPIs) help you figure out the ROI of your robotic cell? You bet!
Your first robot is an important investment. It can open doors to future automation projects – but only if you can prove that the investment was worth it.
If you can't prove that the robot has recovered its costs, your company's commitment to robotics will probably evaporate quicker than water on a hot motor.
But how can you prove that a robot has been a good investment?
We've gone over how to calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) for a planned robot purchase. This calculation is useful at the early stages of robotic cell deployment, but it's only an estimate. It doesn't prove that a certain ROI has been achieved.
To get a more accurate number, you need analytics. This involves using metrics and real operational data. It's a more accurate method, but it can also take longer if you don't measure those metrics properly. Dedicated analytics software can speed up the process significantly.
Here's how to decide which analytics data you will need, gather the data effectively, and analyze it to prove the ROI of your robot.
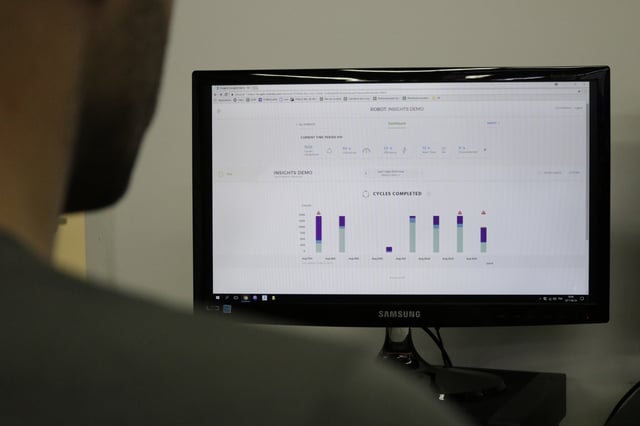 Insights provides the right KPIs for calculating a robot's ROI.
Insights provides the right KPIs for calculating a robot's ROI.
How to use analytics
Not all metrics are equal. There are hundreds, if not thousands, of metrics you could use to measure the effectiveness of your business and robotic system, but only some of them are actually helpful for calculating ROI. You should only use KPIs that are directly linked to the performance of the robotic cell.
Metrics: interesting vs. useful
Make sure you steer clear of metrics that seem interesting, yet are actually useless for measuring robot ROI. Measuring the wrong metric can be worse than measuring no metrics at all, because they'll give you an inaccurate picture of the robot's performance.
For example, let's say you decide to use the "productivity of each cell" metric, so you compare the robot's productivity with the productivity of the other cells to see if it's "keeping up."
Although this might seem like interesting information, it's probably useless, because different cells will have inherently different productivity levels. In this case, it would be much more useful to compare the robotic cell's productivity with the productivity of the previous manual cell (from before it was automated).
Wondering how to make sure you choose the most useful metrics? Keep reading to find out.
Choose the right KPIs
Many of the KPIs we use in business are not directly suited to measuring robot performance. Until recently, there wasn't much information available about how to apply KPIs to collaborative robots.
To address this issue, we've published a new eBook called "The Top 5 Cobot KPIs: How to Measure and Improve the Performance of Collaborative Robots." It explains how KPIs apply to robots, introduces the most useful metrics, and shows you how to measure them.
Download the eBook for a detailed guide to using cobot KPIs.
How the top 5 KPIs relate to the ROI
The top 5 KPIs from the eBook are listed below, along with examples of how they could be linked to your ROI calculations. How you use them specifically will depend on the configuration of your cell.
- Cycle Time—This measures the time it takes for the robot to complete one sequence. It can be used to compare the robot's operation with the previous manual cell's operation. For example, if the robot completes the operation 15% faster than the manual process did, this will soon add up to a lot of time saved. This information could be incorporated into the ROI calculation as part of the total robot working time.
- Cycles Completed—This measures the number of sequences completed with the robot. In many cases, it can indicate how many operations have been successful. You can use it to calculate the process's yield, which could be used in the ROI calculations when calculating scrap costs.
- Utilization—This measures the percentage of time the robot is used, as opposed to the time it sits idle. It can be used to quickly and accurately figure out the robot's downtime for the ROI calculation.
- Efficiency—This indicates how efficiently the robot has been programmed. This can be very useful if your ROI time is longer than expected. For example, if you have an ROI time of 3 years, but your Efficiency is only 20%, then you have strong evidence that improving the robot's programming would also improve the ROI.
- Wait Time—This indicates how much time the robot spends waiting for other processes to finish. High wait times may indicate areas where the ROI of the robot could be improved by optimizing the processes that interact with it.
These five KPIs have been found to directly reflect the performance of collaborative robots, so they're good candidates for making the robot's ROI more accurate.
Record the data
Once you've picked your KPIs, you need to measure them. There are a few ways to do this, but they all fall somewhere between these two ends of the spectrum:
- Infrequent, manual logging—This is where a member of your team manually records the metric from time to time, either with pen and paper or an app. The data are then entered and analyzed with software tools, such as in a spreadsheet or with MES software. Overall, manual logging is usually both inaccurate and time-consuming.
- Automatic logging with cobot-monitoring software—This is where the robot automatically sends relevant data to a centralized software system, which allows you to view and analyze the data in real time. Insights is one such system, and it's specially designed for use with collaborative robots. This method delivers accurate results instantaneously.
The key to recording your KPIs is consistency. Measure them as accurately and as often as possible. For ROI calculations, it makes most sense to use long-term KPI data – meaning data logged over the course of a few weeks, rather than, say, an hour. This is convenient to do in Insights, because you can easily change the time window to view the metrics for an hour, day, week, or even a month.
Calculate ROI
Finally, use your logged KPIs to calculate the ROI for the robotic cell. Although some of the data may be approximations, your metrics will still help provide a more accurate ROI value, as well as clarify the robot's effects on your business.
Download the Lean Robotics ROI Calculator to figure out the return on your robotic cell.





Leave a comment