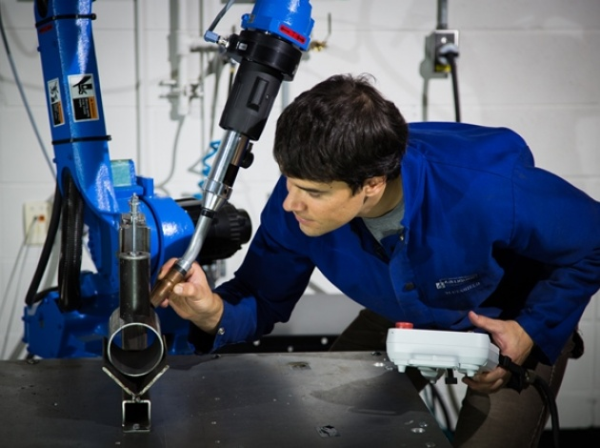
Robotic Welding: What do the Experts say?

Posted on Oct 02, 2013 in Robotic Welding
3 min read time
On September 12, 2013, the Robotic Industries Association (RIA) held an interesting webinar on robotic welding. This presentation explained the basis of robotic welding. Then, for the last 20 minutes, they invited three experts in robotic welding to discuss very interesting questions on the subject. Therefore, we would like to share with you their valuable answers.

The Experts
First, let us introduce you to the panelists.
Mark Oxlade

Mark has been working 25 years for ABB in the Robotic Welding and Cutting Division. He is now a Market Development Manager in the same division.
Unfortunately, due to technical issues, Mark was not able to participate in this discussion.
Joshua Neville

Joshua is a Project Manager at WOLF Robotics. This company is the biggest integrator of ABB welding robots in the world with over 8500 integrations.
Chris Anderson

Chris is a Product Marketing Manager for welding products of Yaskawa/Motoman. He has over 30 years of experience in robotic welding programming.
Question Session
Q1. How much faster does a robot weld versus manual welding?
The panelists agreed that robotic welders can be faster than manual operators with the welding process. However, the main advantage is efficiency. The industrial robots don’t need to take breaks or to stop for lunch. In fact, operators have less than 50% arc-on time and with fatigue, this number decreases as the shift progresses. These types of robots have typically about 75% to 80% arc-on time and, for larger parts with long seams, they can have more than 95% arc-on time.
Q2. How should I start to select a welding robot for my application?
The main criteria would be the size and weight of the part(s) being welded. Its is also important to consider the access to the joint to be welded. This information will help your integrator to know if a standard cell can work for your application or if a customized one is necessary. Often, with the largest parts, tracks and other devices can be required to position the part. Different simulation tools exist such as ABB Studio where the part can be evaluated from its CAD model. It will help to define tooling, cycle time and how to position the part for welding. Moreover, working with aluminum or steel implies different robot and welding packages. Finally, the robotic welding application can also be adjusted with the wanted overall cycle time in order to give the best return on investment.
Q3. How much does a robot welder and a complete system cost?
The average cost for a robot welder is less than 100,000 dollars without the welding equipment. Welding systems can start at 150,000 to 250,000 dollars. It all depends on the complexity of the cell and the part(s) being welded. Robots are cost effective, so the use of multiple robots cell can be justified. Tooling increases significantly the cost of your system. In the end, customized cells are in the range of 250,000 to a couples of million according to the size, payload and complexity of the cell.
The experts were asked 6 more interesting questions on robot welding. In order to know their answers and recommendations, another article will be posted next week.
To be continued...
Robotiq was a proud sponsor of this event since we develop welding devices as well as adaptive end effectors. Learn more about Kinetiq Teaching, a product that will change the way welding robot programming is done.




Leave a comment