Visual Offset Node Accuracy Specifications
Understanding how tag placement and camera distance impact accuracy
The Visual Offset function enables a robot to adjust its movements dynamically based on the detected position and orientation of a reference tag. This is particularly useful in environments where objects or fixtures are not placed with perfect repeatability.
This article explains the expected accuracy of the Visual Offset function and how to maintain high precision by placing the tag at the right location and distance.
Expected Accuracy at a Short Distance
When the distance between the visual offset tag and the camera is ≤ 350 mm, the system can achieve:
-
±3 mm accuracy along the X, Y, and Z axes
-
±1° accuracy in rX, rY, and rZ (rotational) axes
These values are based on controlled testing and represent typical results under good lighting and calibration conditions.
Factors that Affect Accuracy
Several factors influence the actual accuracy:
-
Tag-to-camera distance: Accuracy decreases as this distance increases.
-
Tag size and quality: Larger, high-contrast tags are detected more reliably.
-
Camera resolution and angle: The viewing angle and resolution both impact precision.
-
Lighting conditions: Poor lighting or reflections may introduce noise.
-
Robot motion: Accuracy may degrade during fast or jerky movements.
Coordinate Frame Clarification
Visual Offset outputs six values:
-
X, Y, Z – Translational adjustments in millimeters
-
rX, rY, rZ – Rotational adjustments in degrees
These axes are defined relative to the robot’s camera or user-defined reference frame. Ensure that your expectations are aligned with the framework used in your program.
Best Practices for Visual Offset Placement
To maximize accuracy:
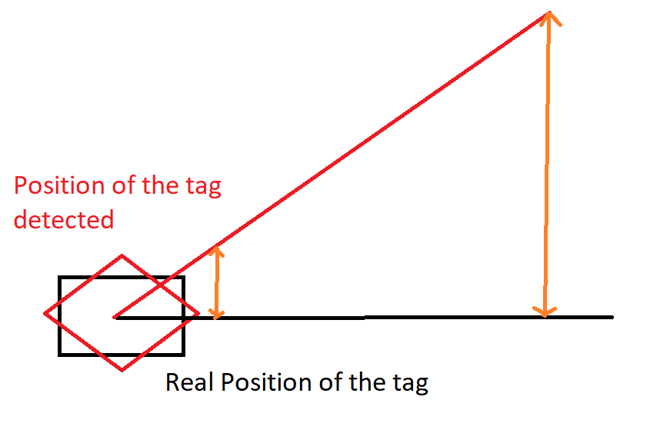
- Place the visual offset tag as close as possible to the point of operation (e.g., pick or place location). If the actions are performed at a higher distance, the precision on the X, Y, and Z axes will therefore not be +/- 3mm of precision but much greater. Here is a diagram that explains this :
-
Keep the tag within 350 mm of the camera during detection.
-
Ensure good lighting and a clear line of sight between the camera and the tag.
-
Avoid oblique angles; try to orient the tag perpendicular to the camera.
-
Calibrate your camera and robot setup before production runs.
Conclusion
To maintain reliable Visual Offset accuracy, keep the tag within 350 mm of the camera and close to the operation point. Always test in your actual environment to validate performance.
Need help? Contact Robotiq Support
Updated: January 2026